Non-Newtonian ViRheometry via Similarity Analysis
Mitsuki Hamamichi1, Kentaro Nagasawa2, Masato Okada2, Ryohei Seto3, Yonghao Yue1,
1Aoyama Gakuin University (AGU) 2The University of Tokyo 3Wenzhou Institute, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences / Oujiang Laboratory
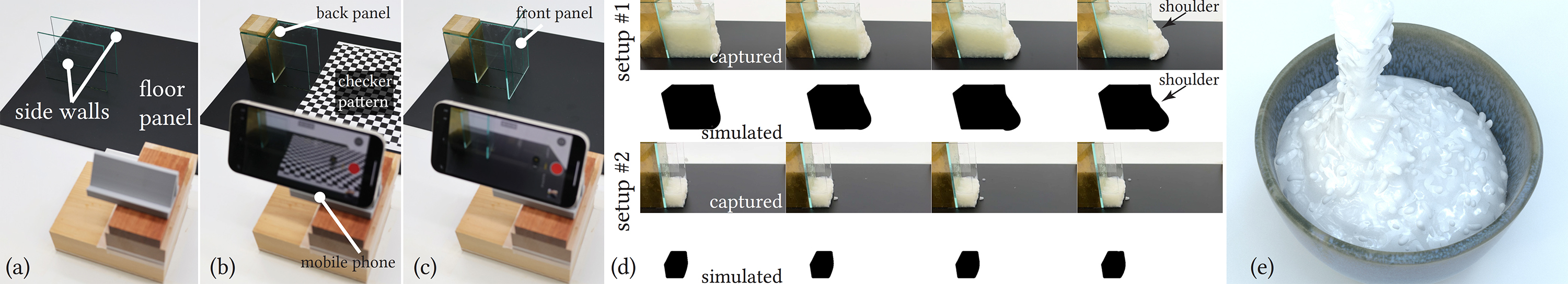
We estimate the three Herschel--Bulkley parameters (yield stress 𝜎Y, power-law index 𝑛, and consistency parameter 𝜂) for shear-dependent fluid-like materials possibly with large-scale inclusions, for which rheometers may fail to provide a useful measurement. We perform experiments using the unknown material for dam-break (or column collapse) setups and capture video footage. We then use simulations to optimize for the material parameters. For better match up with the simple shear flow encountered in a rheometer, we modify the flow rule for the elasto-viscoplastic Herschel–Bulkley model. Analyzing the loss landscape for optimization, we realize a similarity relation; material parameters far away within this relation would result in matched simulations, making it hard to distinguish the parameters. We found that by exploiting the setup dependency of the similarity relation, we can improve on the estimation using multiple setups, which we propose by analyzing the Hessian of the similarity relation. We validate the efficacy of our method by comparing the estimations to the measurements from a rheometer (for materials without large-scale inclusions) and show applications to materials with large-scale inclusions, including various salad or pasta sauces, and congee.
Keywords:Material parameter estimation, Herschel--Bulkley, shear thinning fluids, large-scale inclusions, video-based estimation
Acknowledgements:We thank the anonymous reviewers for their insightful suggestions and discussions. We thank Yuxiang Xiong for helping us with the simulations. This work was supported in part by a grant from JST FOREST Program, JPMJFR206R, Japan, a JSPS Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas 18H05001, Japan, a JSPS Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (A) 18H04106, Japan, a JSPS Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) 21H03448, Japan, a JSPS Grant-in-Aid for Challenging Research (Exploratory) 20K21796, Japan, grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China 12174390 and 12150610463, China, and a grant fromWenzhou Institute, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences WIUCASQD2020002, China.
ACM Trans. Graph. 42, 6, Article 193 (December 2023), 16 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3618310
Paper: PDF (14.9MB)Video: youtube video | High res MP4 (430.7MB)
Supplementary A: PDF (11.1MB)
Supplementary B: PDF (8.4MB)
Codes: Github repository
BibTex
@article{ViRheometry:2023,
author = {Hamamichi, Mitsuki and Nagasawa, Kentaro and Okada, Masato and Seto, Ryohei and Yue, Yonghao},
title = {Non-Newtonian ViRheometry via Similarity Analysis},
year = {2023},
issue_date = {December 2023},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
volume = {42},
number = {6},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3618310},
doi = {10.1145/3618310},
journal = {ACM Trans. Graph. (Proc. of SIGGRAPH Asia 2023)},
articleno = {193},
numpages = {16},
}